In the digital world, financial companies with customer-centric banking culture have the greatest potential to be disruption-proof. Such a bank's culture maximizes chances of success with two basic components: Value and Design. Both of these elements significantly affect the formation of customer-centric excellence within any business. Let’s find out how finance companies can use this knowledge to become customer-centered and conquer the financial industry.
Listen to this article in audio format:
You can download the PDF whitepaper of this artcle with all the graphs and illustrations that help you understand the described processes. Feel free to print it and share it with your colleagues.
What is a Bank Culture and Why it is Important
Culture within a financial organization refers to the values, behaviors, and beliefs that shape the way the organization operates and makes decisions. It includes the company's mission, vision, and goals, as well as the policies, practices, and norms that are in place. A bank culture can also include the way that employees interact with each other and with customers, as well as the level of trust, transparency, and communication within the organization.
The culture of a financial company, particularly a bank culture, can have a significant impact on its success. A positive, customer-centric banking culture can lead to higher levels of customer satisfaction and loyalty, which can translate into increased revenue and profitability. On the other hand, a negative or unethical corporate culture can lead to reputational damage and financial losses, as well as legal and regulatory issues.
For example, if a bank has a culture that prioritizes profits over the needs and well-being of its customers, it may engage in predatory or unethical lending practices, leading to financial harm for its customers and damage to its reputation. On the other hand, if a bank has a culture that values ethical behavior and customer service, it is more likely to have a strong reputation, customer loyalty, and financial success.
In addition to impacting customer relationships and reputation, a bank's culture can also affect the performance and morale of its employees. A positive, supportive work culture can lead to higher levels of employee engagement and productivity, while a negative work culture can lead to high levels of turnover and low morale. Ultimately, the culture of a financial company can have a ripple effect on many aspects of its operations and success.
How Bank Culture is Affected by Value and Design

Value
Value affects the basic guidelines of business leaders, their mindset and the culture of their company. It also impacts the product strategy and the focus of their efforts. In essence, value answers the question of WHY the company exists and what their unique proposal is to their customers.
Design
Design affects how the Value reaches the end user─how it's integrated into the company's products and services. The power and potential of Design is much broader than just a marketing or visual communication tool. We can use Design in research, strategic planning, search for innovations, etc.
Internal and External Perspective
Value and Design both have an internal and an external perspective. The internal perspective of Value is about the main Focus or, in other words, the mindset─what the company considers most important, what it's focused on.
This could be either the desire to get the maximum profit at all costs or an aim to satisfy customers in the best way possible. This has a direct effect on perception. It's based on the passions and values embraced by the founders and leaders of the company.
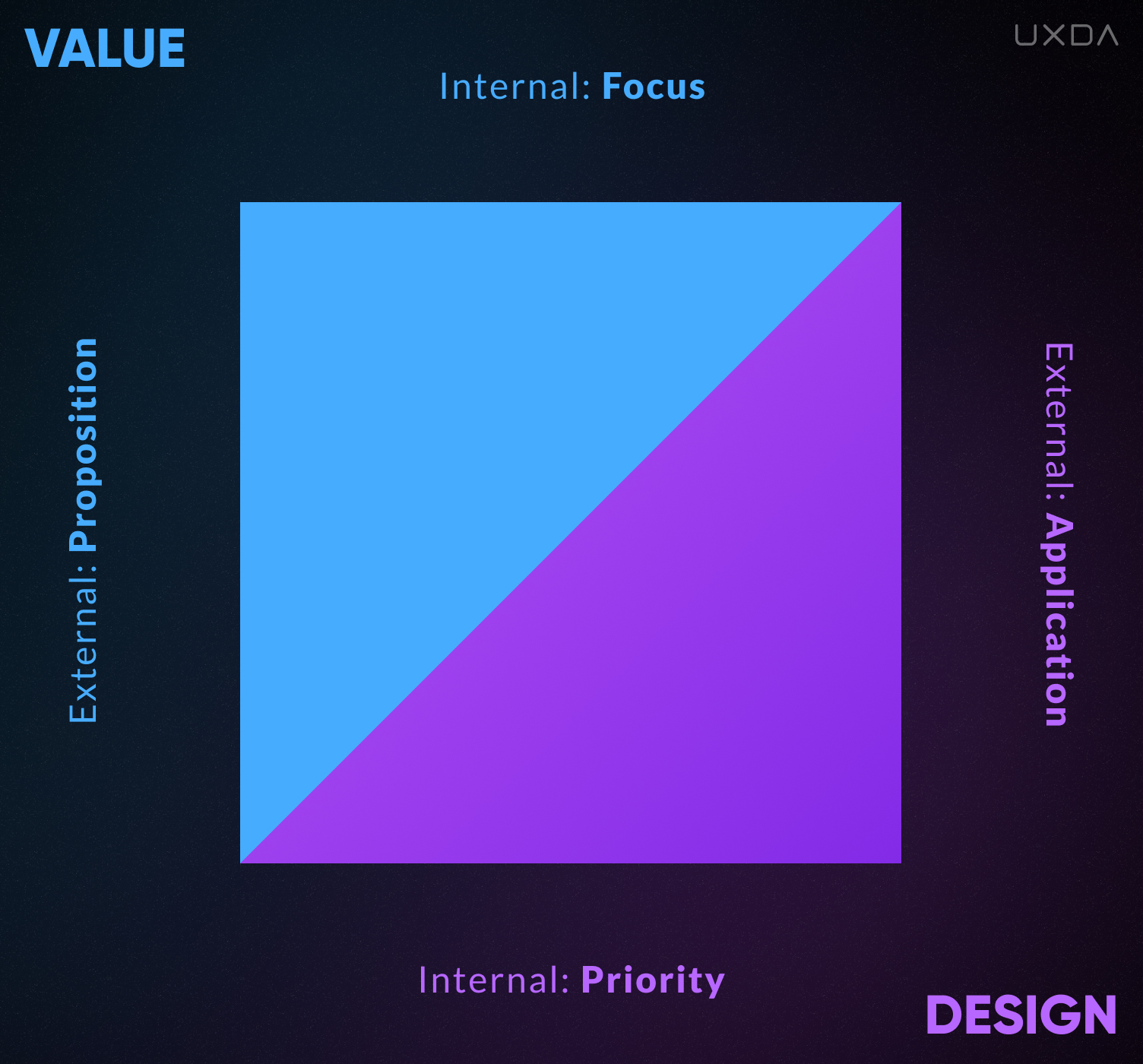
Accordingly, based on the internal Value of the company, an internal attitude to Design is formed. If the company is focusing on profit, design is perceived as a tool. It's one of the company's many operational strategies to gain profit. Usually, at the beginning of its founding, a company is focused on sales and does not have enough experience, competence and knowledge to integrate design at an advanced level. As the company develops, there is a transition to a more mature level.
If the internal Value is focused on the benefit for the customers, then the Design is much more than just a tool. It becomes a roadmap that allows the company to integrate the value of customer-centricity into bank culture and all internal processes. In this case, Design is used as a way of thinking integrated throughout the company to create the best possible solution that meets the consumer needs.
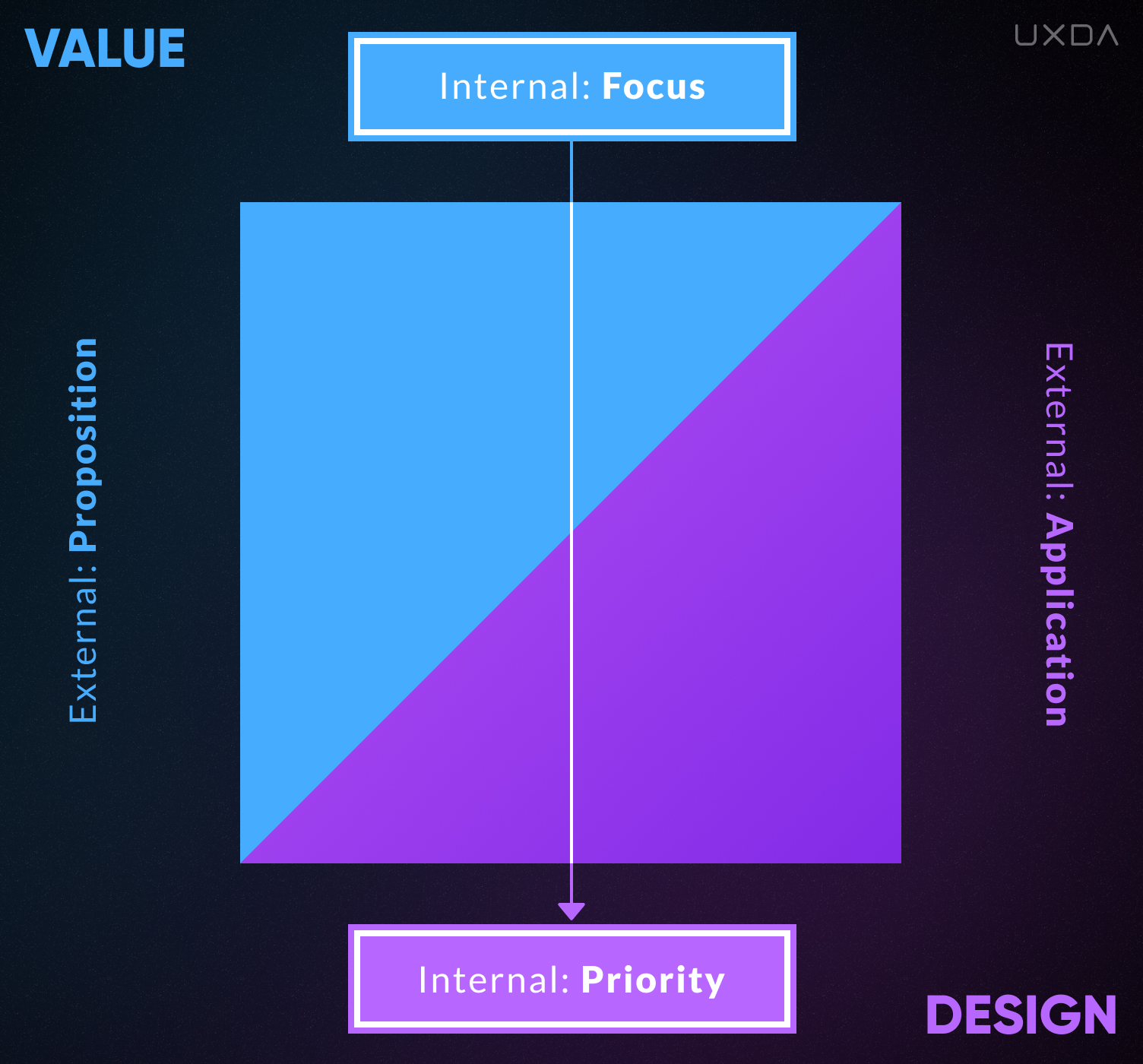
The external part of the Value includes the proposition guidelines on which the offer to the company's customers is built. Аt the beginning, it can be a product that offers only functionality, but at a more mature stage of the business, it becomes a more advanced solution that provides pleasant usability, attractive aesthetics, compliance with a specific status or even a mission to improve the world. These kinds of external attributes not only enhance a product, but provide a valuable and emotionally rich experience for the customers.
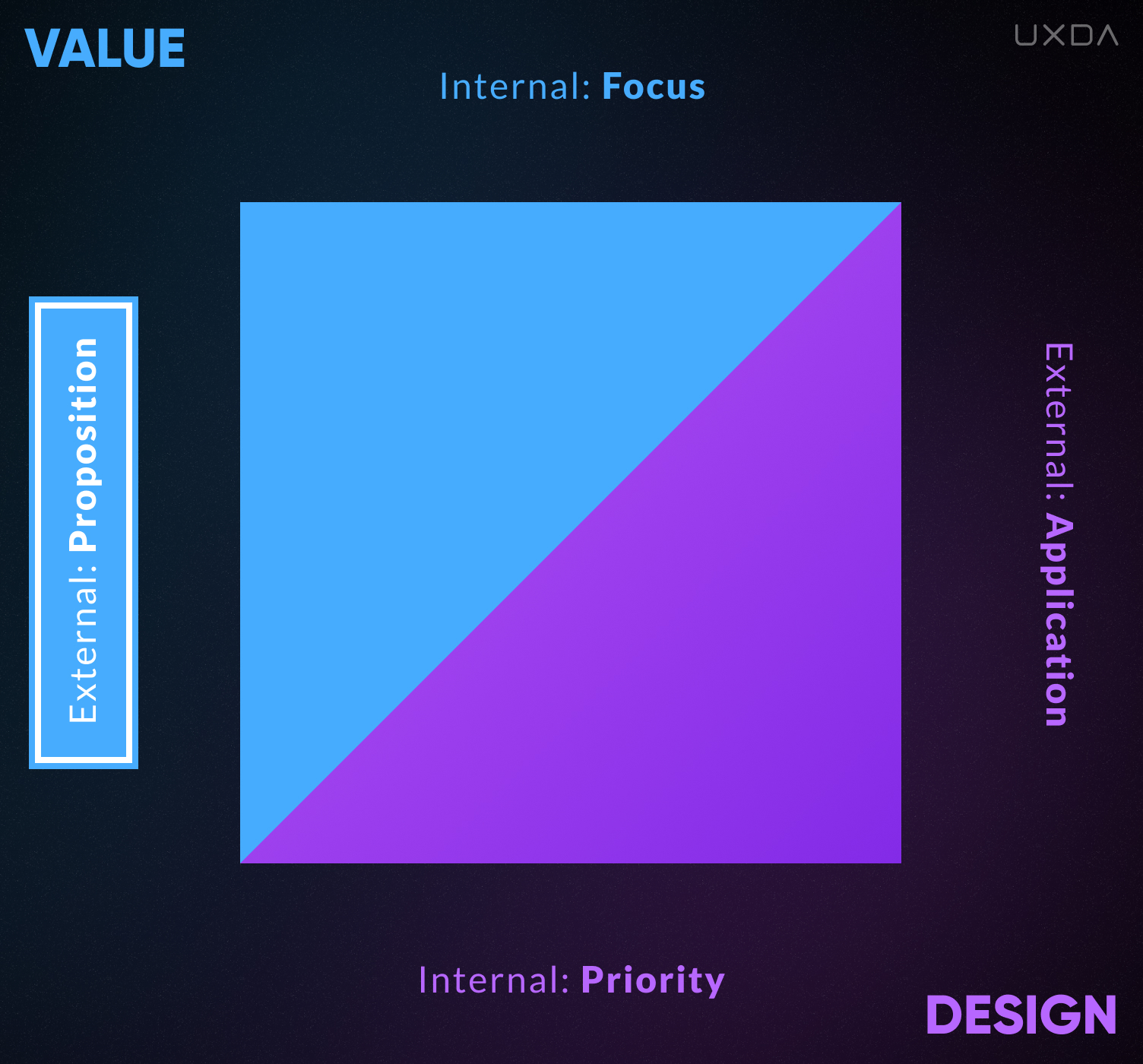
Accordingly, the external manifestation of Value will determine the external side of the Design. If the Value proposition of a product is to offer simple functionality, then Design will be used as visual communication attributes or simply as a pretty package with no added value. In this case, Design creates a background for the product.
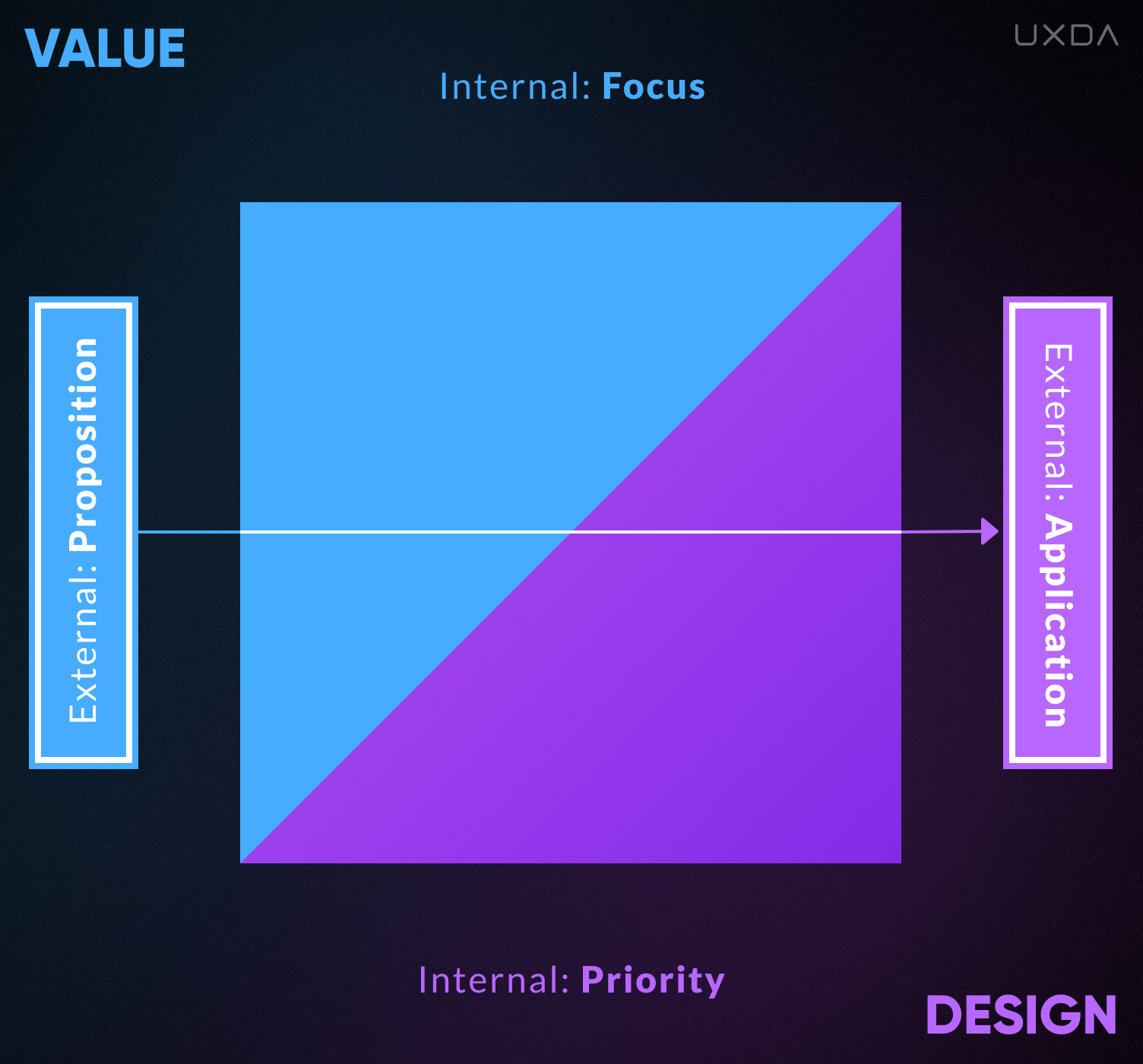
On the other hand, if a company wishes to create a more attractive proposal for its customers, the Value proposition requires a more advanced Design execution. A product that offers a great customer experience and positive emotions, resulting in customer demand and loyalty, can be created using the Design Thinking approach. It means that, in this case, Design becomes the main building material for such a product or service. It's the foundation to create a product that's intuitive, serves customer needs and fills the user journey with pleasant experiences.
We Need a Coordinate System for a Bank Culture
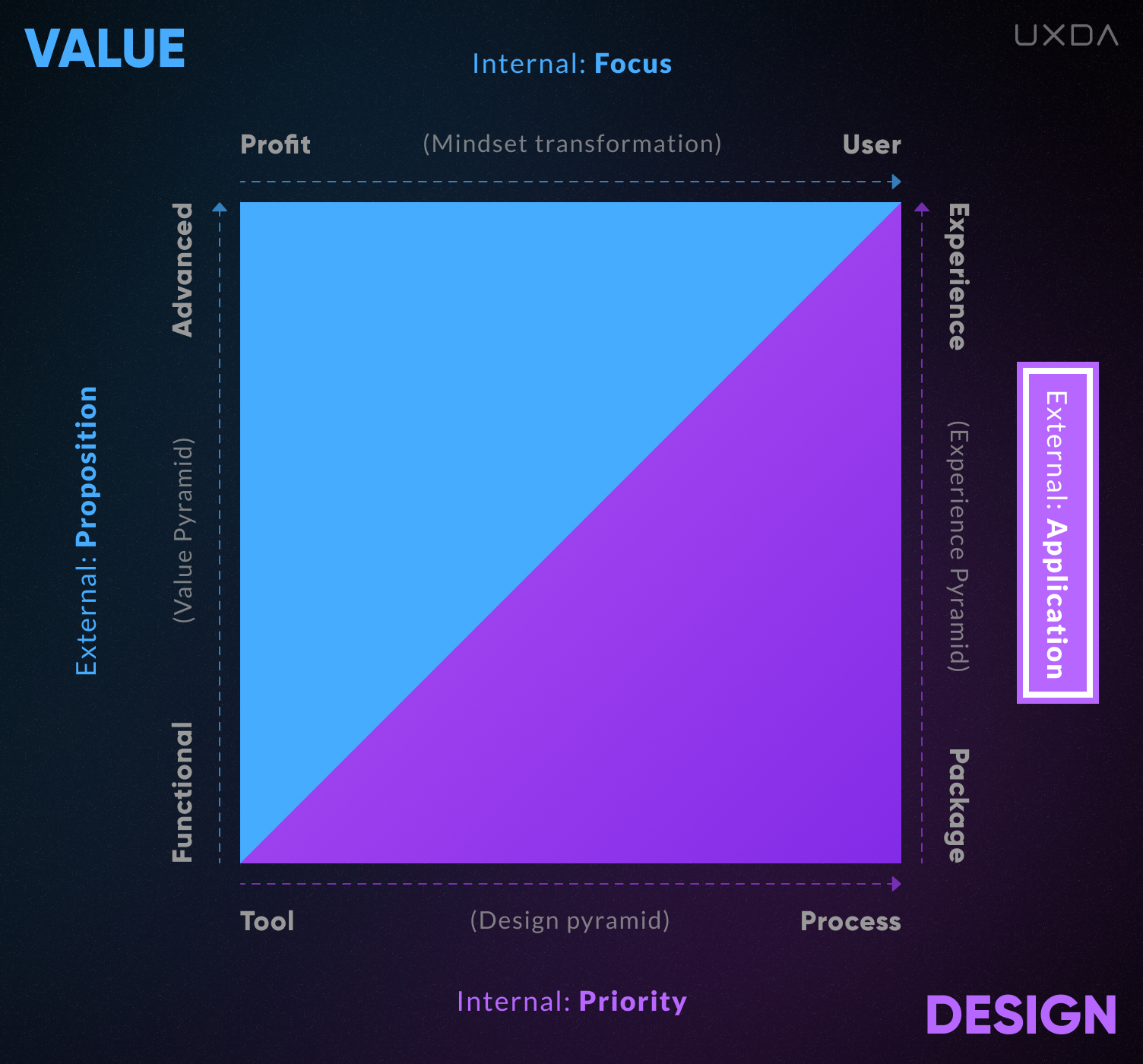
In order to better understand the capabilities and limitations of companies with different types of cultures formed by opposite levels of the above characteristics, we can create a coordinate system.
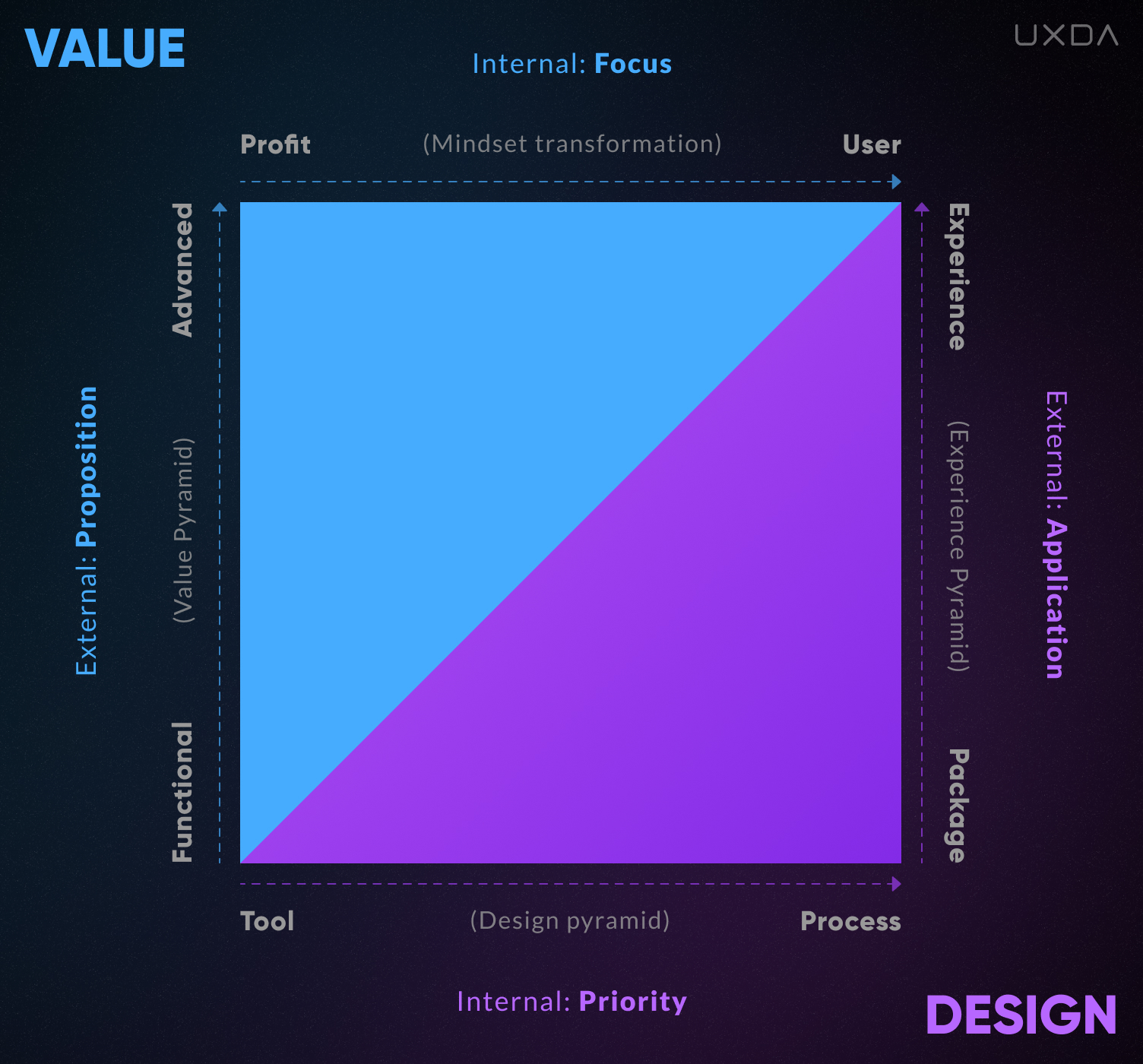
We have two basic vectors: a Value vector and a Design vector, each including an Internal and an External perspective. Respectively, those are divided into four coordinate lines.
1. Value Focus
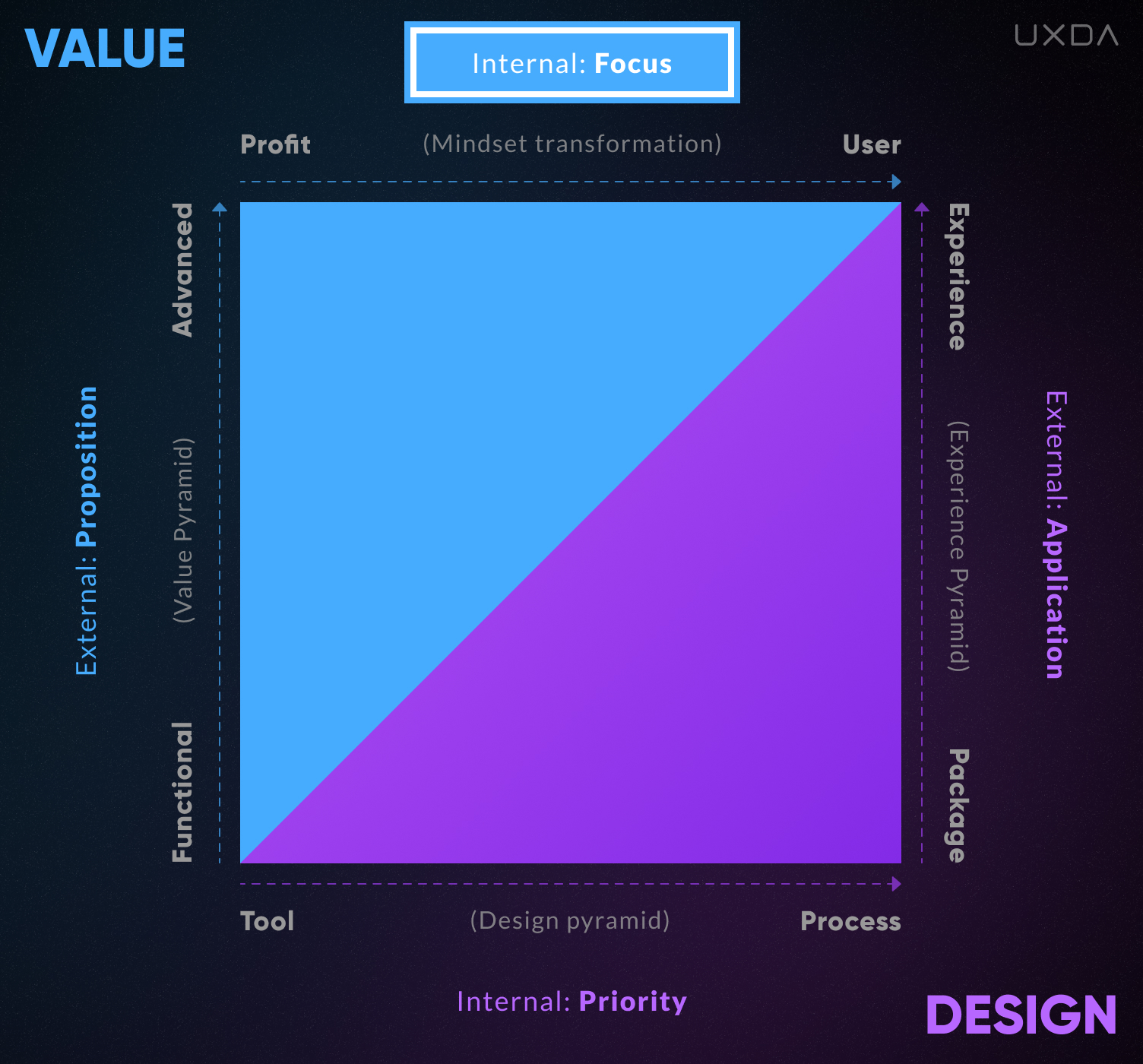
Internal Value Focus is oriented either on profit or on the user. This is the standard way of thinking in a company and the basis of its culture. As with any type of mindset that filters our perceptions, it is characterized by our cognitive biases. In particular, a profit-oriented manager can be so sure that he/she cares about the company’s clients that they will defend this truth with all their might, though actually their actions might, in fact, affect the customers in a negative way.
2. Value Proposition
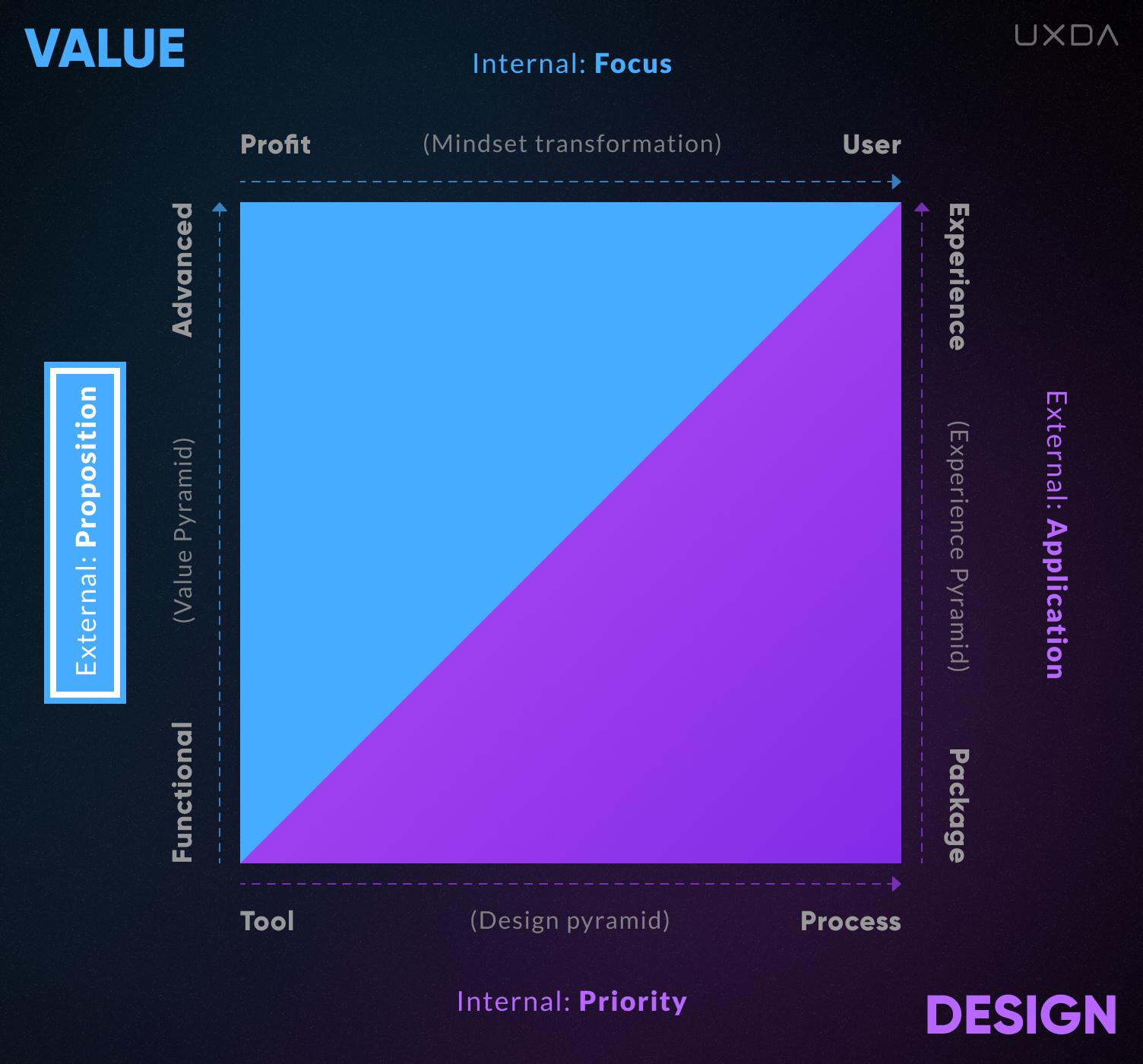
External Value Proposition to consumers, growing from functional to advanced.
3. Design Priority
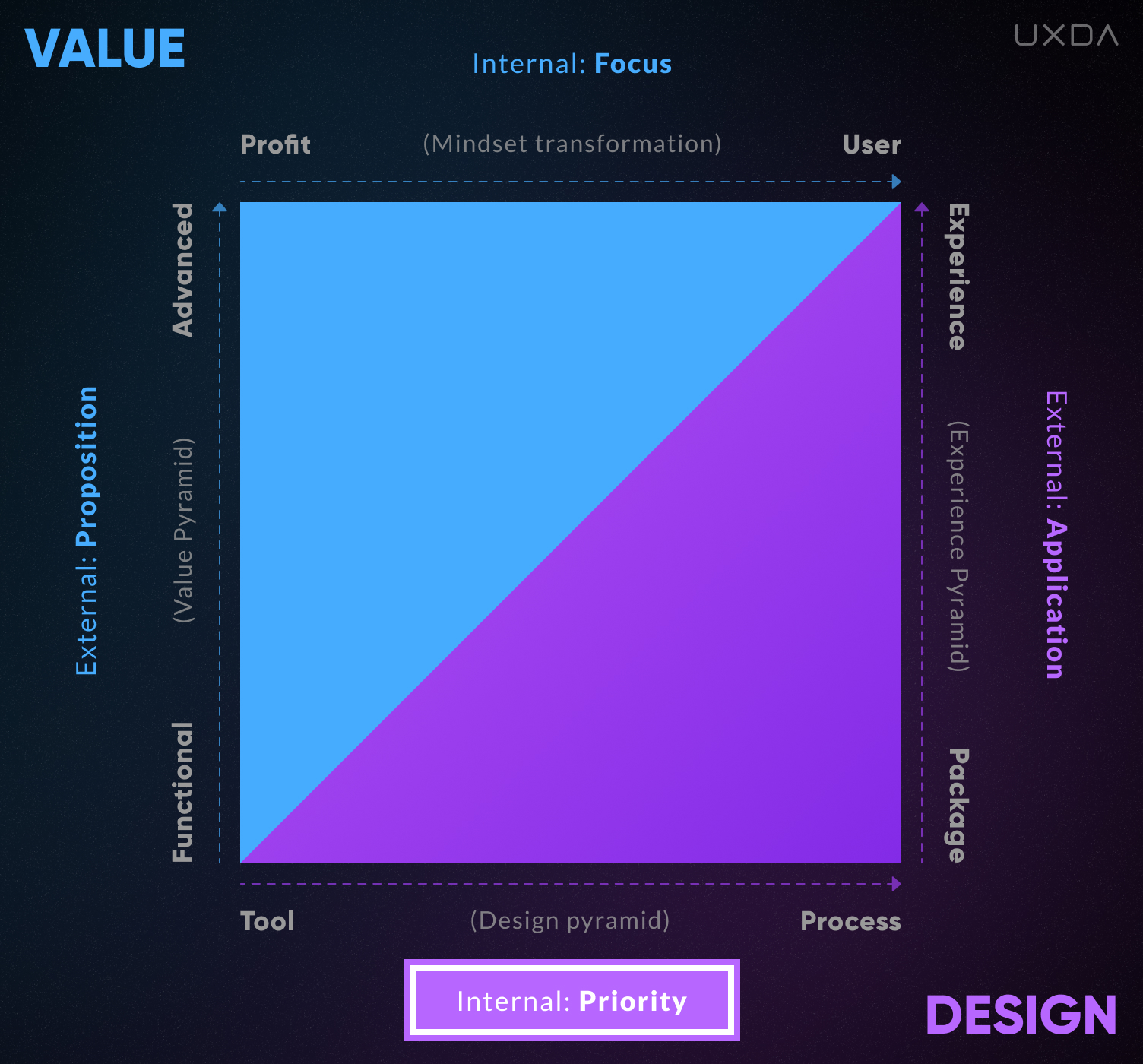
When it comes to Internal Design Priority in the company, Design can be perceived as one of the many business and marketing tools or as a key process integrated into the bank's culture DNA.
4. Design Application
The External Design Application dictates whether the Design is used to create product packaging─mainly visual communication─or defining the creation of a product or a service and its further development, resulting in the best customer experience.
Four Types of Banking Culture Based on Value and Design
At the intersection of these four coordinates, we get four quadrants in which certain cultural characteristics prevail, creating four basic types of cultures.
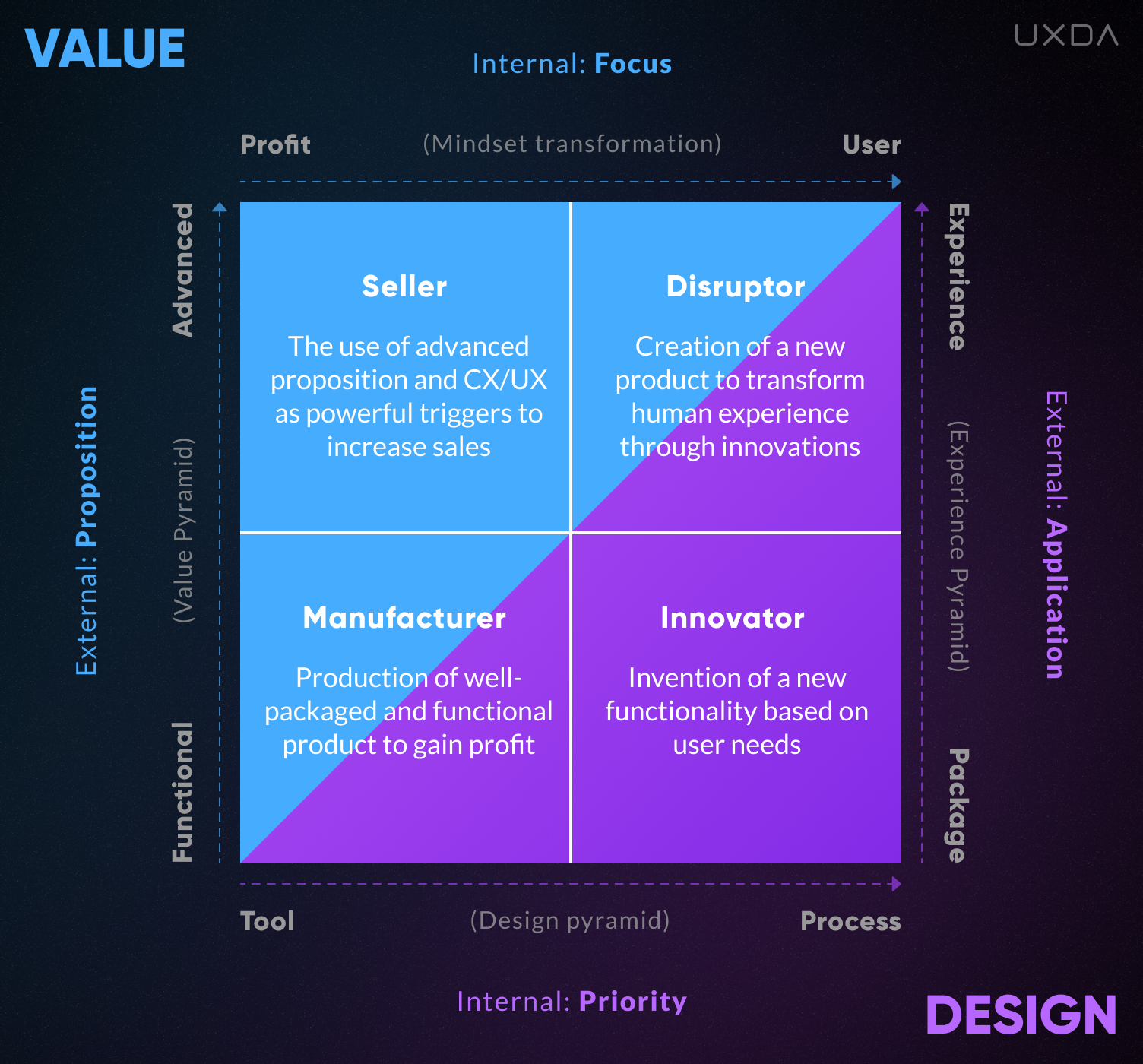
1. Manufacturer
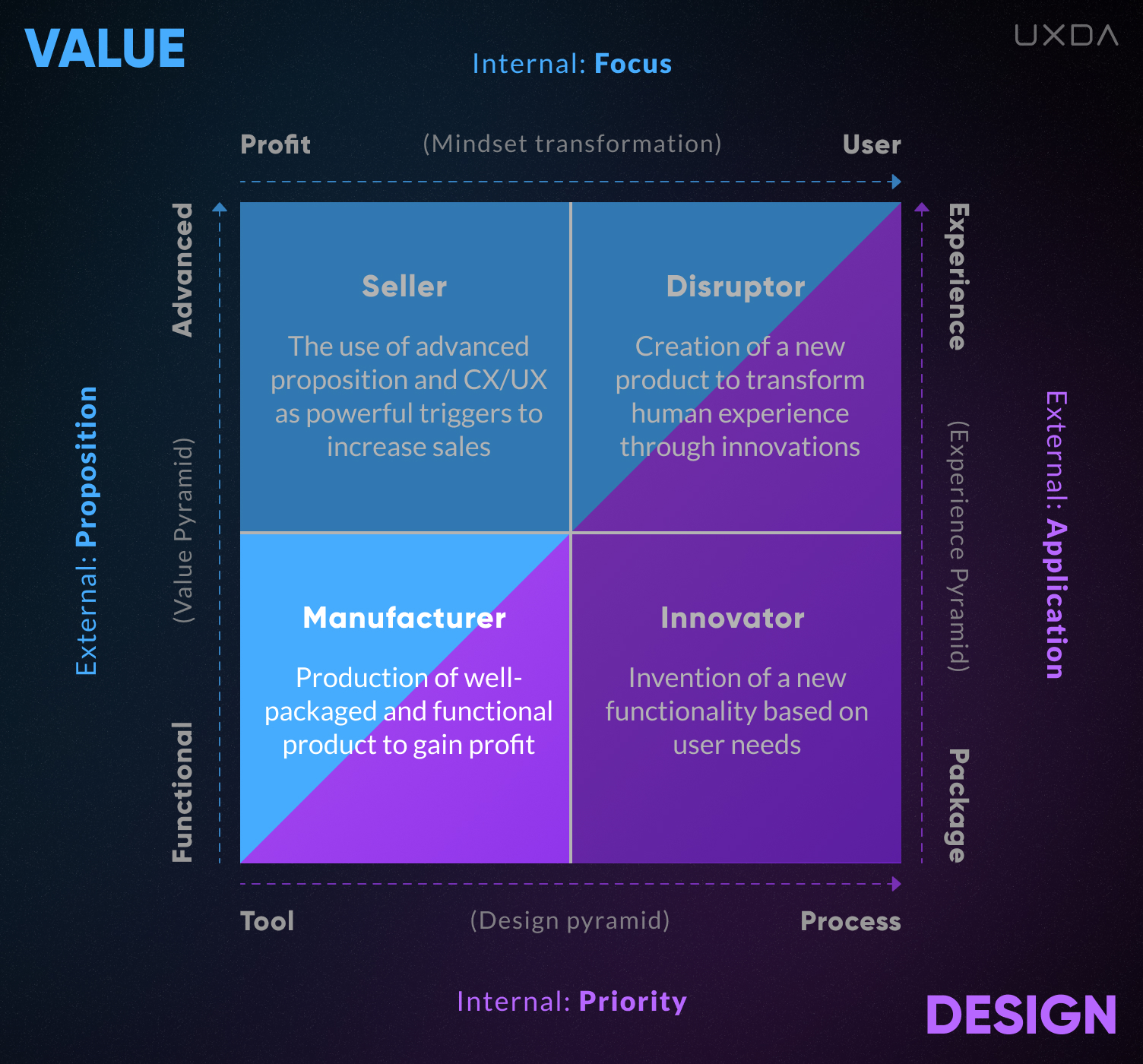
The lower left quadrant characterizes the classic Manufacturer. This is a company that cares more about its profit and production process than its customers. Against the backdrop of the efforts invested in product creation and standardization of production, the interests of consumers do not seem so important.
Therefore, the management of this company is convinced that basic functionality is enough for users. Design, in this case, is a tool that is needed to create packaging, to bring the product to the market in an attractive way.
The manufacturing company is an outdated type of organization culture that excelled in the industrial age. Today, it is rapidly losing its position in the market, often not understanding why it is happening.
They follow a basic formula: multiplying the functionality of a product by a competent business model and adding massive market distribution.

Unfortunately, in the digital world, this formula is no longer effective. It is necessary to take into account the increased influence of users, competition and a decrease in market barriers caused by global digitalization.
The plan for an effective transformation of the Manufacturer culture includes:
- switching the mindset from profit-oriented to user-oriented;
- reviewing the role of design in the company in order to turn it into a growth factor that improves product quality;
- reinventing the company's product or service according to an advanced value proposition, thus going beyond the limits of functional competition, occupying a unique niche in the “blue ocean” of uniqueness and possibilities.
This is only possible if the company is focused on providing the best possible customer experience. The Manufacturer must understand that the functional level and beautiful packaging are not enough to establish a connection with their clients. They will appreciate only a well-designed customer journey that solves their problems, eases their daily lives and brings pleasant experiences.
After all, any customer problem caused by an unfriendly product can quickly become the source of a bad experience. Due to the network effect, social networks and review aggregators, this can spoil the reputation of the whole company and its products in just minutes.
Methodology to use:
2. Seller
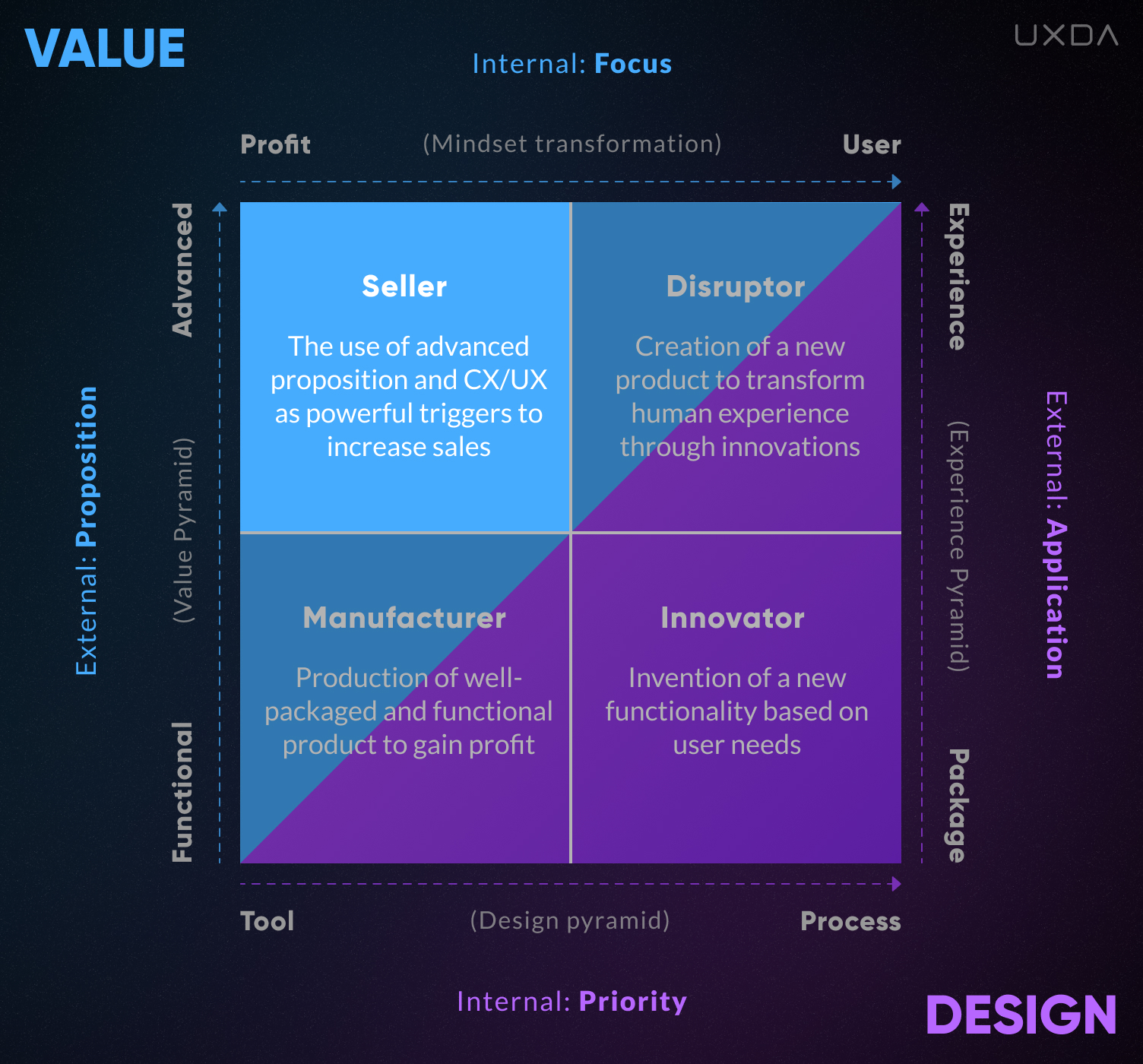
The Seller culture is located in the upper left quadrant. Unlike the Manufacturer, it is not so focused on providing only functionality to its customers. The Seller collects data about customers, finding out their preferences and needs. Then this information is further used by a marketing department that develops advanced communication strategies according to the customer expectations to address them on an emotional level.
Sellers are well aware that, in conditions of high competition, it is necessary to use something more attractive to users than boring and standardized functionality.
Therefore, they use an advanced value proposition and user interaction design as powerful promotional triggers.
The functionality of the product is not improved this way, as most of the efforts made by the Seller are most often ornamental. This is aimed at attracting consumers’ attention to create an illusion of novelty.
Despite all the client-centered slogans of such companies, their customers don't feel they are concerned about their interests, face formal attitude, poor service and could possibly even become victims of ethical violations─manipulations aimed at short-term profit growth. After all, the consumer for such a company is only an object for making a purchasing decision, and the company's priority is to increase conversion using any available tools.
Employees of such enterprises are well aware of this. According to Medallia survey, while 78 percent of the surveyed employees reported that delighting customers is a top priority of their company’s leadership, nearly 60 percent also reported that their companies don’t really listen to them. 24% said their companies use front-line suggestions to improve customer experience once a year or less; one-third complained that management never takes action based on customer feedback. Only less than half of employees said they can count on their leader- ship to remove obstacles to delighting customers.
For the Seller’s culture, a user-oriented mindset is a blind spot, and that becomes a key weakness. Company executives look at other successful businesses with high customer loyalty and satisfaction, as well as motivated employees. They try to guess and imitate the secret to their success, but, without the proper Design approach and mindset integrated into the company's culture, it's nearly impossible.
The problem is that, instead of sincerely understanding how to help customers and how to improve their experience, Sellers are trying to use a customer-centered approach as a magical way to increase profits.
As a result, despite all the efforts and invested resources, the company often faces negative customer attitudes, fails at digital transformation and, ultimately, loses its market position.
In this case, a successful transformation depends on the willingness to change the basic guidelines of the business, the culture of the organization and goal setting. Each employee should rethink their role in the company, making their customers a top priority.
In this case, the profit will be an organic indicator of the quality of service and raising customer satisfaction.
To do this, a company should make the customer-centered design approach the number one priority by integrating it at all levels, starting with business processes. Further, at the team level, there should be people who are experts in applying the design approach for the product to meet the customer needs. People responsible for Design in the company should have the proper support and authority in the company. For the company to succeed, it is critical that the business executives and key leaders share the same understanding and facilitate the importance of user-centricity and Design approach throughout every process and employee.
Further, it is necessary to clearly understand the duties of the design facilitators of the company. This is not just about performing basic package design work. It's the ability to integrate the Design approach and Design thinking into the core principles of the company. Such an activity can take the business to a whole new level, but it's also important to define how the success will be measured.
For example, a sales-oriented company associates its metrics with the level of conversion and the number of leads, prospects, sales and retention. At the same time, important points are ignored, such as:
- user feedback;
- the number and reasons for complaints about the service;
- the number of users who recommend the product to friends;
- the number of positive and negative comments about the company on social media platforms.
It's crucial to use these long-term oriented metrics to get a real picture instead of believing self-created “fake news” that the product is successfully sold and brings good dividends.
As you see during the transformation, it is necessary to rethink performance indicators and bring to the forefront metrics related to customer satisfaction. So, you can change the internal guidelines and involve the entire company in a customer-centered experience transformation. The final task of the company is to purposefully seek what their product lacks and improve upon that instead of trying to mask these “imperfections” with attractive marketing.
Methodology to use:
3. Innovator
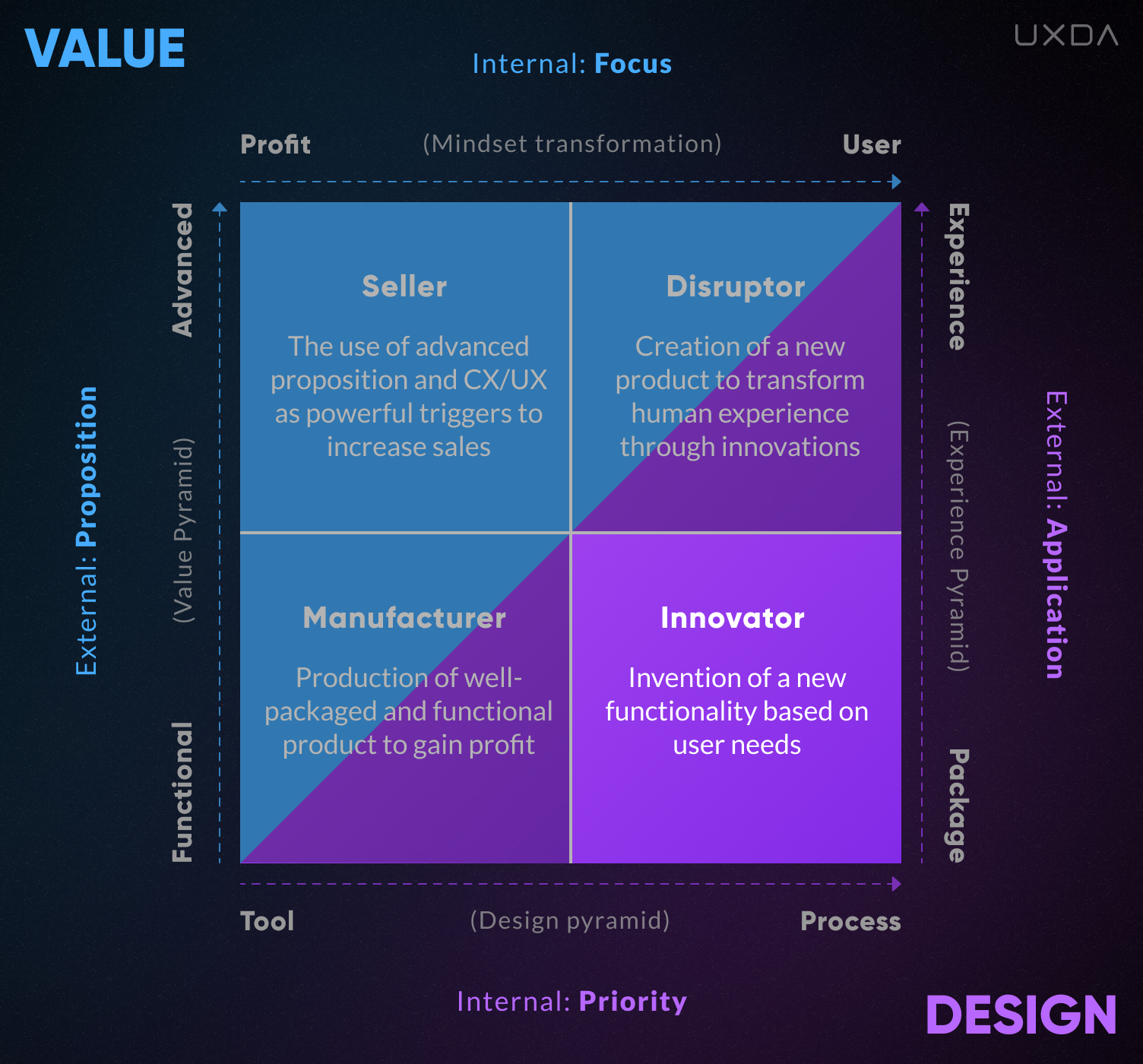
In the lower right quadrant are Innovator company culture. As part of this classification, by Innovators, I mean user-oriented entrepreneurs who make technological improvements. These are usually engineering companies looking for technical solutions that will better meet the needs of consumers to provide them with extra functionality.
They use Design thinking as a creative process aimed at finding problem-solving ideas. Innovators are sure that the functionality of a new level provides high value for consumers. Therefore, they are much more interested in researching and developing a new technology than caring about the customer experience.
That’s why there are usually other companies that later use the Innovator’s ideas and inventions to create beautiful and convenient products based on this innovative technology.
The difficulties of Innovators are related to the fact that the development of new functionality is a key process for them, and they are not ready to delve into the psychology and consumer behavior. As a result, the first products of the Innovator’s companies are inconvenient and interesting only to a narrow circle of specialists and technology geeks.
The Innovator team uses the Design process to search for new ideas that would bring brand-new possibilities for the users. They utilize technology to improve people's lives, and their goal is to bring benefit to the world, not to sell the product to the masses in any way possible.
If they had more resources, then perhaps they would be able to attract more consumers with a better user experience and, as a result, disrupt the industry.
For the success-aimed culture transformation, it is necessary to remove the idea that functionality is enough and understand that the main value for people is the experience. Using the existing consumer orientation, it is necessary to take an additional step and orient the new technology, primarily to create a better experience for the customers.
UXDA’s methodology to use:
4. Disruptor
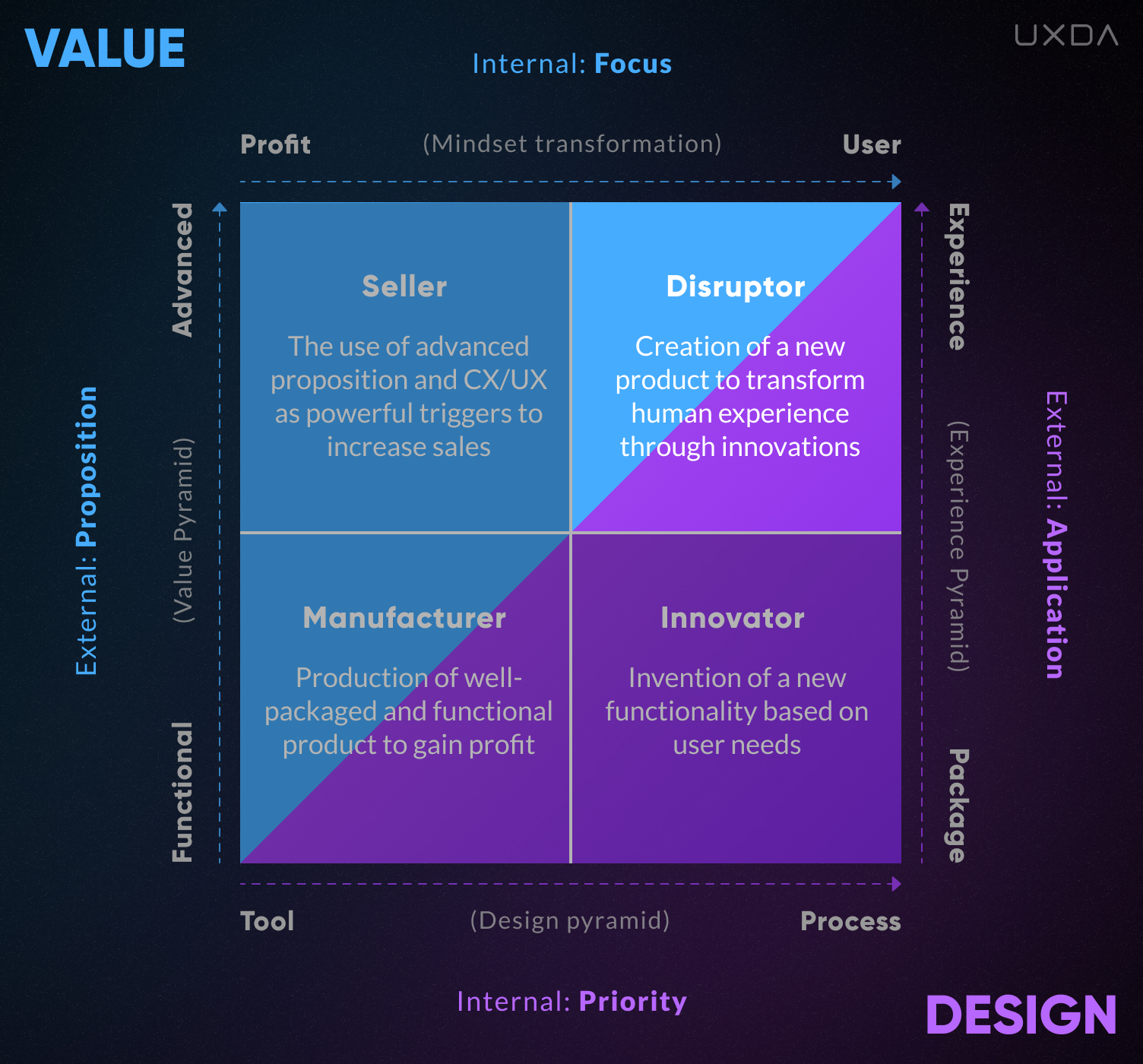
Disruptors are companies that change the traditional way an industry operates to a new and more effective way. To do this, they engage the maximum potential of all four vectors aimed at the realization of the purpose through the ultimate customer-centricity. Very often, they are perceived as companies changing markets or even creating new markets through disruptive innovations. These are companies with purpose-driven culture that reinvent experience, offering something new that is much more convenient, efficient and enjoyable than the boring alternatives already available on the market.
Disruptors see profit as the result of maximum user satisfaction, and as a result of realizing the purpose of the company that is focused on customers’ benefits.
They do not compromise for profit because they have very strict internal ethics associated with providing the best service and social responsibility.
This provides them with long-term competitive advantages, customer loyalty and community support, all of which results in above-average profits.
Purpose-driven companies often use the functionality that Innovators have created but develop it at the higher levels of the Value Proposition. Being obsessed with execution, purpose-driven culture brings every element of the user experience to perfection. Such companies main task is not so much to create innovative technologies, but rather to rethink the habitual way of life. And, that is what makes them true Disruptors.
They realize the maximum potential of their business model, product and market offer through the integration of a Design approach into the company's culture DNA. Thanks to this, Disruptors are able to build the most trusting relationships with their customers, and, in case of any business difficulties, they receive support and assistance from their fans.
Such a company is related to UXDA’s Digital Product Success Formula:
Will You Become the Next Purpose-Driven Financial Disruptor?
As you see, a Disruptor in this classification is not necessarily a huge corporation or the technology giant that disrupts the traditional industries with enormous budgets. The principles and approach to purpose-driven business culture described here are already used to create demanded products and competitive advantages in a wide variety of industries.
As an example, we can check the small businesses that, due to their customer centricity, have gained undeniable advantages in the local market. In particular, in almost every city, we can find a restaurant that offers unforgettable service and pays so much attention to creating positive experiences with its customers that, after visiting, everyone tells their friends about it, thus providing free advertising.
It is no miracle of phenomena. It is simple math that anyone can study and integrate into their own business, regardless of whether it's a huge corporation or a tiny startup, to start reaping significant benefits. All it takes is a true dedication to satisfy customers in the best way possible by creating an unforgettable customer experience.
Additional answers that might be helpful:
How can a financial institution influence its banking culture?
There are a number of ways that a financial organization can create a positive and supportive banking culture that helps its employees to thrive and contribute to the organization's success:
- Establishing a clear set of values and principles that guide the organization's actions and decisions.
- Encouraging a positive and inclusive work environment that promotes collaboration and diversity.
- Providing training and development opportunities to help employees develop the skills they need to succeed.
- Implementing effective performance management systems that provide feedback and support to employees.
- Establishing clear policies and procedures to ensure compliance with laws, regulations, and ethical standards.
- Promoting open communication and encouraging employees to speak up and share their ideas and concerns.
- Providing leadership that is transparent, approachable, and supportive of employee development.
What are the main benefits of a customer-centric banking culture in a financial institution?
A customer-centric banking culture can provide a number of benefits to a financial organization:
Improved customer satisfaction
By focusing on the needs and preferences of customers, a financial organization can deliver a better customer experience and increase customer satisfaction.
Increased customer loyalty
When customers feel that they are valued and their needs are being met, they are more likely to remain loyal to the organization. This can lead to increased customer retention and reduced acquisition costs.
Greater market share
A positive customer experience can differentiate a financial organization from its competitors and attract new customers. This can help the organization to grow its market share and increase its revenue.
Enhanced reputation
A customer-centric culture can help a financial organization to build a positive reputation, which can attract new customers and partners, and make the organization more attractive to employees.
Greater employee satisfaction
Employees who feel that their efforts are aligned with the needs of customers are likely to be more engaged and motivated. This can lead to higher levels of employee satisfaction and retention.
What are the main challenges in implementing a customer-centric banking culture?
There can be several challenges to implementing a customer-centric banking culture in a financial organization:
1. Changing organizational culture
Establishing a customer-centric culture may require significant changes to the way the organization operates. This can be difficult to achieve and may require significant time and resources.
2. Aligning employees with the new culture
It is important to ensure that all employees understand and support the customer-centric culture. This may require training and development to help employees understand the importance of customer service and the role they play in delivering it.
3. Balancing customer needs with business goals
While it is important to focus on the needs of customers, it is also important to ensure that the organization's business goals are met. This can be a challenge when trying to implement a customer-centered culture.
4. Managing customer expectations
A customer-centric culture may lead to increased customer expectations, which can be difficult to manage. It is important to ensure that the organization has the resources and capabilities to meet these expectations.
5. Maintaining momentum
Establishing a customer-centric culture is an ongoing process, and it is important to maintain the momentum and focus on customer service over the long term. This can be challenging, especially when facing competing priorities or changing market conditions.
What are the main differences in how "Manufacturer," "Seller," "Innovator," and "Disruptor" banking cultures approach customer experience?
Here are the main differences in how "Manufacturer", "Seller", "Innovator", and "Disruptor" banking cultures approach customer experience, based on the provided excerpt from "Bank Culture: Transforming Banking with the UX Matrix":
Manufacturer Culture
- Prioritizes profit and production process over customer needs. Management believes basic functionality is sufficient for users.
- Views design as a tool for packaging and marketing, rather than for improving the customer experience.
- Outdated model struggling in the digital world where user influence and competition are high.
- Transformation requires shifting focus to user needs, integrating design to improve products, and offering more than just functional value.
Seller Culture
- Collects customer data to inform marketing strategies that target emotions and create an illusion of novelty.
- Focuses on using design as a promotional trigger to increase conversion, rather than genuinely improving the customer experience.
- Prioritizes short-term profit growth and may engage in manipulative tactics.
- Lacks a genuine user-oriented mindset despite customer-centric slogans.
- Transformation requires a genuine shift to customer-centricity, integrating design thinking into core principles, and prioritizing customer satisfaction metrics.
Innovator Culture
- Engineering-driven companies focused on developing new technology to better meet customer needs.
- Prioritizes research and development of innovative functionality over customer experience.
- May create products that are initially inconvenient for mainstream users.
- Transformation requires recognizing the importance of customer experience and designing technology to create a better experience.
Disruptor Culture
- Purpose-driven companies that prioritize customer-centricity and offer innovative solutions that improve the customer experience.
- Sees profit as a result of user satisfaction and realizing the company's purpose of benefiting customers.
- Maintains high ethical standards and social responsibility.
- Integrates design into the company's culture and aims to rethink traditional ways of doing things.
Get UXDA Research-Based White Paper "How to Win the Hearts of Digital Customers":
 If you want to create next-gen financial products to receive an exceptional competitive advantage in the digital age, contact us! With the power of financial UX design, we can help you turn your business into a beloved financial brand with a strong emotional connection with your clients, resulting in success, demand, and long-term customer loyalty.
If you want to create next-gen financial products to receive an exceptional competitive advantage in the digital age, contact us! With the power of financial UX design, we can help you turn your business into a beloved financial brand with a strong emotional connection with your clients, resulting in success, demand, and long-term customer loyalty.
- E-mail us at info@theuxda.com
- Chat with us in Whatsapp
- Send a direct message to UXDA's CEO Alex Kreger on Linkedin




















